Creating Xen and KVM RHEL 5 Virtual Machines from the Command-line (virt-install and virsh)
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Creating an RHEL 5 KVM Virtual Machine | Managing and Monitoring RHEL 5 based KVM Guest Systems |
|
You are reading a sample chapter from the RHEL 5 Edition book. Purchase the fully updated Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 (RHEL 8) Edition of this publication in eBook ($9.99) or Print ($36.99) format Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Essentials Print and eBook (ePub/PDF/Kindle) editions contain 31 chapters and over 250 pages |
In the previous chapter we explored the creation of KVM guest operating systems on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 host using the virt-manager graphical tool. Whilst this graphical tool does much to ease the virtual machine creation process, there are some drawbacks to this approach. Perhaps the most significant shortcoming is that the graphical tool does not provide any way to automate creation of virtual machines. In addition, virt-manager can only be used where access to a graphical desktop environment is available. In the case of headless servers, however, this is not always the case.
In this chapter, therefore, we will turn our attention to the creation of KVM and Xen based virtual machines using the virt-install and virsh command-line tools. These tools provide all the capabilities of the virt-manager utility with the added advantage that they can be used within scripts to automate virtual machine creation. In addition, the virsh command allows virtual machines to be created based on a specification contained within a configuration file.
The virt-install tool is supplied to allow new virtual machines to be created by providing a list of command-line options. This chapter assumes that the necessary KVM or Xen tools are installed. For details on these requirements read Installing KVM Virtualization on RHEL 5 or Installing and Configuring RHEL 5 Xen Virtualization.
Running virt-install to build the KVM or Xen Guest System
The virt-install utility must be run as root and accepts a wide range of command-line arguments that are used to provide configuration information related to the virtual machine being created. Some of these command-line options are mandatory (specifically name, ram and disk storage must be provided) while others are optional. A summary of these arguments is outlined in the following table:
|
Argument |
Description |
|---|---|
| -h, --help | Show the help message and exit |
| --connect=CONNECT | Connect to a non-default hypervisor. |
| -n NAME, --name=NAME | Name of the new guest virtual machine instance. This must be unique amongst all guests known to the hypervisor on the connection, including those not currently active. To re-define an existing guest, use the virsh(1) tool to shut it down (’virsh shutdown’) & delete (’virsh undefine’) it prior to running "virt-install". |
| -r MEMORY, --ram=MEMORY | Memory to allocate for guest instance in megabytes. If the hypervisor does not have enough free memory, it is usual for it to automatically take memory away from the host operating system to satisfy this allocation. |
| --arch=ARCH | Request a non-native CPU architecture for the guest virtual machine. The option is only currently available with QEMU guests, and will not enable use of acceleration. If omitted, the host CPU architecture will be used in the guest. |
| -u UUID, --uuid=UUID | UUID for the guest; if none is given a random UUID will be generated. If you specify UUID, you should use a 32-digit hexadecimal number. UUID are intended to be unique across the entire data center, and indeed world. Bear this in mind if manually specifying a UUID |
| --vcpus=VCPUS | Number of virtual cpus to configure for the guest. Not all hypervisors support SMP guests, in which case this argument will be silently ignored |
| --check-cpu | Check that the number virtual cpus requested does not exceed physical CPUs and warn if they do. |
| --cpuset=CPUSET | Set which physical cpus the guest can use. "CPUSET" is a comma separated list of numbers, which can also be specified in ranges. If the value ’auto’ is passed, virt-install attempts to automatically determine an optimal cpu pinning using NUMA data, if available. |
| --os-type=OS_TYPE | Optimize the guest configuration for a type of operating system (ex. ’linux’, ’windows’). This will attempt to pick the most suitable ACPI & APIC settings, optimally supported mouse drivers, virtio, and generally accommodate other operating system quirks. See "--os-variant" for valid options. For a full list of valid options refer to the man page (man virt-install). |
| --os-variant=OS_VARIANT | Further optimize the guest configuration for a specific operating system variant (ex. ’fedora8’, ’winxp’). This parameter is optional, and does not require an "--os-type" to be specified. For a full list of valid options refer to the man page (man virt-install). |
| --host-device=HOSTDEV | Attach a physical host device to the guest. HOSTDEV is a node device name as used by libvirt (as shown by ’virsh nodedev-list’). |
| --sound | Attach a virtual audio device to the guest. (Full virtualization only). |
| --noacpi | Override the OS type / variant to disables the ACPI setting for fully virtualized guest. (Full virtualization only). |
| -v, --hvm | Request the use of full virtualization, if both para & full virtualization are available on the host. This parameter may not be available if connecting to a Xen hypervisor on a machine without hardware virtualization support. This parameter is implied if connecting to a QEMU based hypervisor. |
| -p, --paravirt | This guest should be a paravirtualized guest. If the host supports both para & full virtualization, and neither this parameter nor the "--hvm" are specified, this will be assumed. |
| --accelerate | When installing a QEMU guest, make use of the KVM or KQEMU kernel acceleration capabilities if available. Use of this option is recommended unless a guest OS is known to be incompatible with the accelerators. The KVM accelerator is preferred over KQEMU if both are available. |
| -c CDROM, --cdrom=CDROM | File or device use as a virtual CD-ROM device for fully virtualized guests. It can be path to an ISO image, or to a CDROM device. It can also be a URL from which to fetch/access a minimal boot ISO image. The URLs take the same format as described for the "--location" argument. If a cdrom has been specified via the "--disk" option, and neither "--cdrom" nor any other install option is specified, the "--disk" cdrom is used as the install media. |
| -l LOCATION, --location=LOCATION | Installation source for guest virtual machine kernel+initrd pair. The "LOCATION" can take one of the following forms:
|
| --pxe | Use the PXE boot protocol to load the initial ramdisk and kernel for starting the guest installation process. |
| --import | Skip the OS installation process, and build a guest around an existing disk image. The device used for booting is the first device specified via "--disk" or "--file". |
| --livecd | Specify that the installation media is a live CD and thus the guest needs to be configured to boot off the CDROM device permanently. It may be desirable to also use the "--nodisks" flag in combination. |
| -x EXTRA, --extra-args=EXTRA | Additional kernel command line arguments to pass to the installer when performing a guest install from "--location". |
| --disk=DISKOPTS | Specifies media to use as storage for the guest, with various options. |
| --disk opt1=val1,opt2=val2,... | To specify media, one of the following options is required:
|
| -f DISKFILE, --file=DISKFILE | Path to the file, disk partition, or logical volume to use as the backing store for the guest’s virtual disk. This option is deprecated in favor of "--disk". |
| -s DISKSIZE, --file-size=DISKSIZE | Size of the file to create for the guest virtual disk. This is deprecated in favor of "--disk". |
| --nonsparse | Fully allocate the storage when creating. This is deprecated in favort of "--disk" |
| --nodisks | Request a virtual machine without any local disk storage, typically used for running ’Live CD’ images or installing to network storage (iSCSI or NFS root). |
| -w NETWORK, --network=NETWORK | Connect the guest to the host network. The value for "NETWORK" can take one of 3 formats:
|
| -b BRIDGE, --bridge=BRIDGE | Bridge device to connect the guest NIC to. This parameter is deprecated in favour of the "--network" parameter. |
| -m MAC, --mac=MAC | Fixed MAC address for the guest; If this parameter is omitted, or the value "RANDOM" is specified a suitable address will be randomly generated. For Xen virtual machines it is required that the first 3 pairs in the MAC address be the sequence ’00:16:3e’, while for QEMU or KVM virtual machines it must be ’54:52:00’. |
| --nonetworks | Request a virtual machine without any network interfaces. |
| --vnc | Setup a virtual console in the guest and export it as a VNC server in the host. Unless the "--vncport" parameter is also provided, the VNC server will run on the first free port number at 5900 or above. The actual VNC display allocated can be obtained using the "vncdisplay" command to "virsh" (or virt-viewer(1) can be used which handles this detail for the use). |
| --vncport=VNCPORT | Request a permanent, statically assigned port number for the guest VNC console. Use of this option is discouraged as other guests may automatically choose to run on this port causing a clash. |
| --sdl | Setup a virtual console in the guest and display an SDL window in the host to render the output. If the SDL window is closed the guest may be unconditionally terminated. |
| --nographics | No graphical console will be allocated for the guest. Fully virtualized guests (Xen FV or QEmu/KVM) will need to have a text console configured on the first serial port in the guest (this can be done via the --extra-args option). Xen PV will set this up automatically. The command ’virsh console NAME’ can be used to connect to the serial device. |
| --noautoconsole | Don’t automatically try to connect to the guest console. The default behaviour is to launch a VNC client to display the graphical console, or to run the "virsh" "console" command to display the text console. Use of this parameter will disable this behaviour. |
| -k KEYMAP, --keymap=KEYMAP | Request that the virtual VNC console be configured to run with a non- English keyboard layout. |
| -d, --debug | Print debugging information to the terminal when running the install process. The debugging information is also stored in "$HOME/.virtinst/virt-install.log" even if this parameter is omitted. |
| --noreboot | Prevent the domain from automatically rebooting after the install has completed. |
| --wait=WAIT | Amount of time to wait (in minutes) for a VM to complete its install. Without this option, virt-install will wait for the console to close (not neccessarily indicating the guest has shutdown), or in the case of --noautoconsole, simply kick off the install and exit. Any negative value will make virt-install wait indefinitely, a value of 0 triggers the same results as noautoconsole. If the time limit is succeeded, virt-install simply exits, leaving the virtual machine in its current state. |
| --force | Prevent interactive prompts. If the intended prompt was a yes/no prompt, always say yes. For any other prompts, the application will exit. |
| --prompt | Specifically enable prompting. Default prompting is off (as of virtinst 0.400.0) |
|
You are reading a sample chapter from the RHEL 5 Edition book. Purchase the fully updated Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 (RHEL 8) Edition of this publication in eBook ($9.99) or Print ($36.99) format Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Essentials Print and eBook (ePub/PDF/Kindle) editions contain 31 chapters and over 250 pages |
An Example RHEL 5 virt-install Command
With reference to the above command-line argument list, we can now look at an example command-line construct using the virt-install tool.
Note that in order to be able to display the virtual machine in a graphical console, the virt-viewer package must be installed on the RHEL host. This can be achieved by executing the following command in a terminal window:
yum install virt-viewer
The following command creates a new KVM or Xen virtual machine configured to run Windows 7 using full virtualization. It creates a new, 10GB disk image, assigns 1024MB of RAM to the virtual machine, configures a CD device for the installation media and uses VNC to display the console:
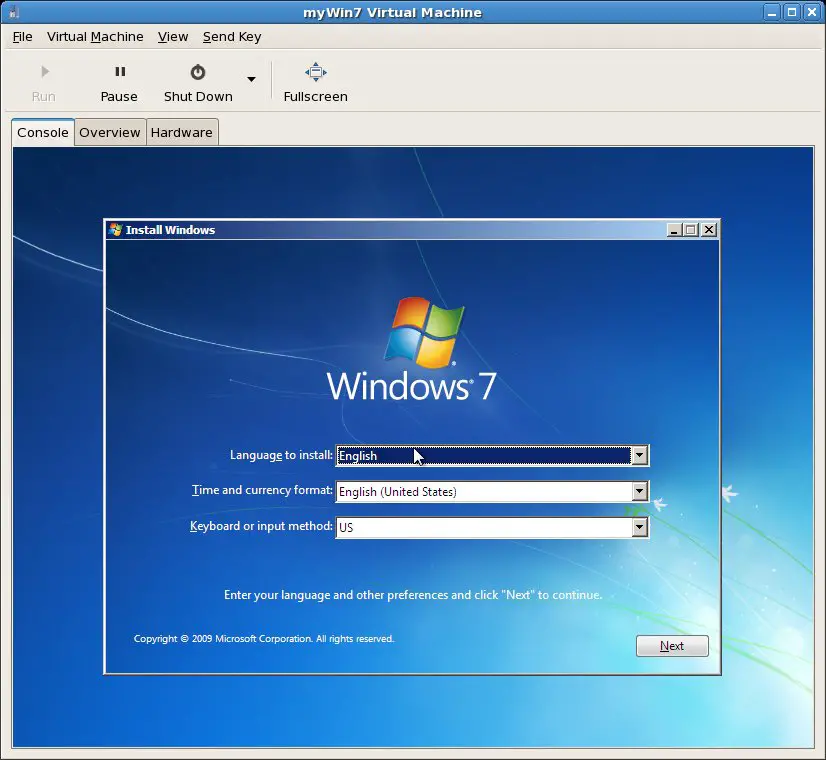
virt-install --name myWin7 --hvm --ram 1024 --disk path=/tmp/win7.img,size=10 --network network:default --vnc --os-variant vista --cdrom /dev/hda
Note that the above command line assumes the installation media is in a drive corresponding to device file /dev/hda. This may differ on your system, or may be replaced by a path to an ISO image file residing on a file system.
As the creation process runs, the virt-install command will display status updates of the creation progress:
Starting install... Creating storage file... | 10.0 GB 00:00 Creating domain... | 0 B 00:00 Domain installation still in progress. Waiting for installation to complete.
Once the guest system has been created, the virt-viewer screen will appear containing the operating system installer loaded from the specified installation media:
Follow the standard installation procedure for the guest operating system.
Starting and Stopping a Virtual Machine from the Command Line
Having created the virtual machine from the command line it stands to reason that you may also need to start it from the command line in the future. This can be achieved using the virsh command line utility, referencing the name assigned to the virtual machine during the creation process. For example:
virsh start myWin7
Similarly, the virtual machine may be sent a shutdown signal as follows:
virsh shutdown myWin7
If the virtual machine fails to respond to the shutdown signal and does not begin a graceful shutdown the virtual machine may be destroyed (with the attendant risks of data loss) using the destroy directive:
virsh destroy myWin7
Creating a Virtual Machine from a Configuration File
The virsh create command can take as an argument the name of a configuration file on which to base the creation of a new virtual machine. The configuration file uses XML format. Arguably the easiest way to create a configuration file is to dump out the configuration of an existing virtual machine and modify it for the new one. This can be achieved using the virsh dumpxml command. The following command outputs the configuration data for a virtual machine domain named WindowsVM to a file named WindowsVM.xml:
virsh dumpxml WindowsVM > WindowsVM2.xml
Once the file has been generated, load it into an editor to review and change the settings for the new virtual machine:
<domain type='xen'>
<name>WindowsVM</name>
<uuid>e33fe24c-0d84-9323-f278-6a949aff0807</uuid>
<memory>1048576</memory>
<currentMemory>1048576</currentMemory>
<vcpu>1</vcpu>
<os>
<type arch='x86_64' machine='xenfv'>hvm</type>
<loader>/usr/lib/xen/boot/hvmloader</loader>
<boot dev='hd'/>
</os>
<features>
<acpi/>
<apic/>
<pae/>
</features>
<clock offset='localtime'/>
<on_poweroff>destroy</on_poweroff>
<on_reboot>restart</on_reboot>
<on_crash>restart</on_crash>
<devices>
<emulator>/usr/lib64/xen/bin/qemu-dm</emulator>
<disk type='file' device='disk'>
<driver name='file'/>
<source file='/var/lib/xen/images/WindowsVM.img'/>
<target dev='hda' bus='ide'/>
</disk>
<disk type='block' device='cdrom'>
<driver name='phy'/>
<source dev='/dev/hda'/>
<target dev='hdc' bus='ide'/>
<readonly/>
</disk>
<interface type='bridge'>
<mac address='00:16:36:63:a6:de'/>
<source bridge='virbr0'/>
<script path='vif-bridge'/>
</interface>
<serial type='pty'>
<target port='0'/>
</serial>
<console type='pty'>
<target port='0'/>
</console>
<input type='tablet' bus='usb'/>
<input type='mouse' bus='ps2'/>
<graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport='yes' keymap='en-us'/>
</devices>
</domain>
A variety of settings can be changed. For example the virtualization type, domain name, memory allocation, number of CPUs and the location of the disk image file to name but a few options. At the very least, the domain name and image file must be changed in order to avoid conflict with the virtual machine from which the configuration was taken. Once the file has been modified, the new virtual machine may be created as follows:
virsh create WindowsVM2.xml
|
You are reading a sample chapter from the RHEL 5 Edition book. Purchase the fully updated Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 (RHEL 8) Edition of this publication in eBook ($9.99) or Print ($36.99) format Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Essentials Print and eBook (ePub/PDF/Kindle) editions contain 31 chapters and over 250 pages |
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Creating an RHEL 5 KVM Virtual Machine | Managing and Monitoring RHEL 5 based KVM Guest Systems |