Managing and Monitoring Fedora based Xen Guest Systems
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Installing and Configuring Fedora Xen Virtualization | Installing a Xen Guest OS from the Command-line (virt-install) |
Take your Fedora Linux Skills to the Next Level |
In the previous chapter (Installing and Configuring Fedora Xen Virtualization) we covered the steps necessary to configure the Fedora operating system to act as a Xen host system and created, installed and ran a Xen guest system.
In this chapter we will explore the use of the virt-manager tool to manage the Xen guest operating systems.
Starting and Stopping Xen Guest Systems
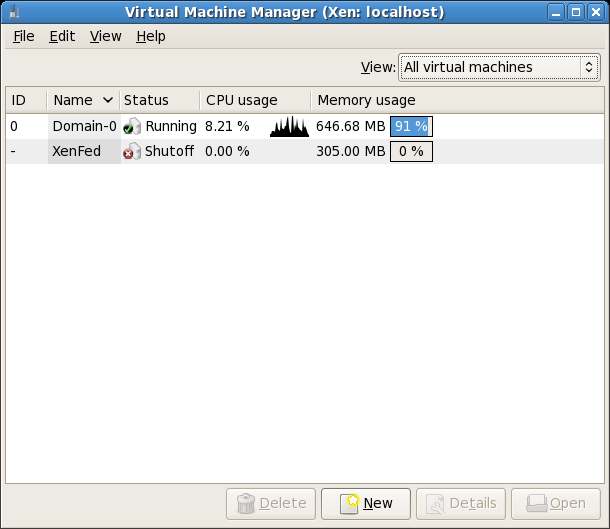
When a Xen guest operating system has been configured it will appear in the list of systems when the virt-manager is loaded. The virt-manager tool is launched either by selecting the Applications->System Tools->Virtual Machine Manager menu option or from the command-line by running /usr/sbin/virt-manager.
The following screenshot shows the virt-manager tool running on a Fedora system. It lists two systems - Domain 0 which is the host system, and a guest system named XenFed which is currently shut down:
To stop a virtual machine running a guest OS it is not sufficient to simply close the Virtual Machine Console and Virtual Machine Manager windows. Doing so only closes the manager and console, leaving the guest operating system running in the background. In fact, if you try closing these windows and then restart the virt-manager tool you will see the guest OS is still listed as running, and selecting open will display the guest OS exactly as it was before you closed the console window.
To shutdown a guest OS, either shut it down using the operating system's own shut down mechanism, click on Shutdown in the Virtual Machine Console toolbar, or right click on the guest OS from the list in the virt-manager main screen and select Shutdown.
Pausing a Xen Guest Operating System
Xen provides the ability to pause and resume a running guest operating system. To pause a running system, either click the Pause button in the Virtual Machine Console toolbar, or right click the operating system in the virt-manager main screen and select Pause.
A paused guest OS may then be resumed either by clicking again on the Pause button in the Virtual Machine Console toolbar, or right click the operating system in the virt-manager main screen and select Resume.
Note that a paused guest system will not survive the reboot of the host operating system and continues to use system memory in the paused state. In the event that the host operating system is rebooted, the guest operating system will need to be restarted and cannot be resumed from its paused state.
To save a session which can be restored in its current state at any point in the future (including after a host system reboot use the xm suspend and resume options):
xm suspend guestname
To restore a session:
xm resume guestname
Changing Xen Guest Operating System Settings
During the initial configuration of the guest OS in virt-manager a number of resources such as memory allocation and CPU usage were defined. It is common to discover after the guest OS starts running that these settings need to be changed. Fortunately, virt-manager makes it easy to change these settings.
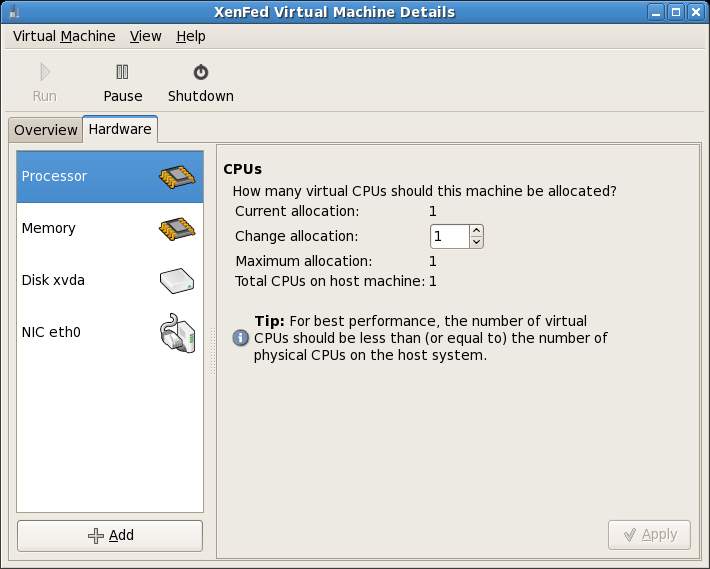
To modify the settings for a specific guest operating system, start virt-manager (Applications->System Tools->Virtual Machine Manager), select the desired guest operating system and click on the Details button. When the Virtual Machine Details dialog appears, click on the Hardware tap to view the current settings:
The hardware screen initially displays the CPU settings, allowing the number of CPUs used by the virtual machine to be modified.
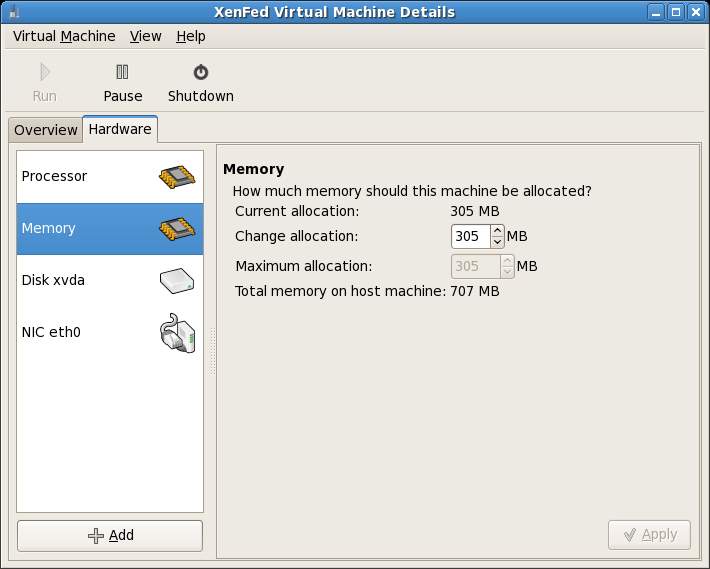
The panel on the left allows the current displayed category to be changed. For example, to change the memory assigned to the guest system, select the Memory option and change the settings as required:
Additional disks may be added by clicking on the Add button at the bottom of the hardware category list, selecting Storage device from the Hardware type menu and clicking on Forward. Specify either a disk partition, or a file location to act as the new disk.
Monitoring Virtual Machine Performance
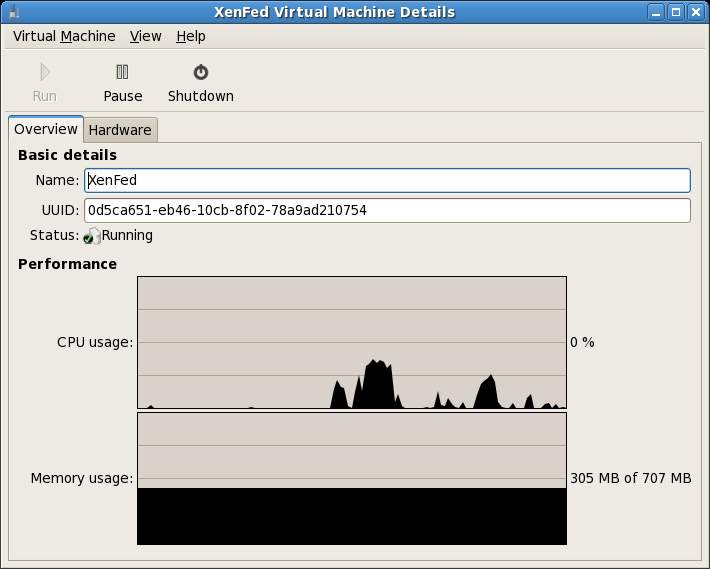
The virt-manager tool provides information on CPU and memory usage for each guest operating system. To view the performance graphs, select the desired guest OS in the virt-manager main window and click on Details. The Virtual Machine Details screen will display two real-time graphs showing the Memory and CPU usage for the selected guest:
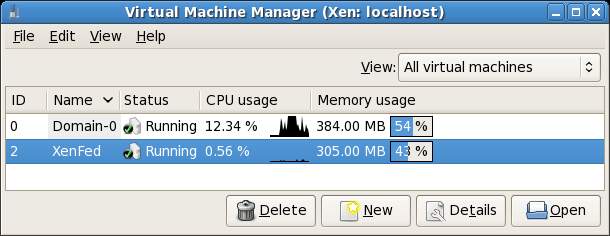
In addition, the virt-manager main window displays smaller CPU graph and Memory scales next to each guest OS together with a bar indicating the percentage of overall available memory used by each operating system:
The overall performance statistic of the host operating system may similarly be viewed by selecting the host OS in virt-manager (typically Domain-0) and clicking Edit->Machine details....
Take your Fedora Linux Skills to the Next Level |