Basic Fedora Linux Firewall Configuration
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Configuring Fedora Linux Wireless Networking | Using Firestarter to Configure a Fedora Linux Firewall |
A firewall is a vital component in protecting a computer system, or network of computers from external attack (typically from an internet connection). Any computer connected directly to an internet connection must run a firewall to protect against malicious activity. Similarly, any internal network must have some form of firewall between it and an external internet connection.
Fedora Linux is supplied with powerful firewall technology known as iptables built-in. Entire books can, and indeed have, been written about configuring iptables. If you would like to learn about iptables we recommend Linux Firewall Configuration - Packet Filtering and iptables.
Fortunately Fedora Linux also provides some tools which make firewall configuration for the average user easy. This chapter will cover the steps necessary to configure a Fedora Linux firewall using those tools.
Fedora Linux Firewall Options
Fedora Linux provides two firewall configuration options. The first is a basic yet effective and easy to use firewall configuration system called Security Level Control. Another, more advanced, option is called Firestarter. And yet another option is to use a tool called Guarddog.
In this chapter we will explore the Security Level Control and in the next chapter (Using Firestarter to Configure a Fedora Linux Firewall) we will look at the Firestarter firewall configuration tool in more detail.
Configuring a Basic Fedora Linux Firewall
To launch the Security Level Configuration tool, open the desktop System menu and click on Firewall and SELinux option of the Administration sub-menu. Alternatively, the tool can be launched from the command-line as follows:
system-config-securitylevel
Enter your password when prompted. Once loaded, the security level tool should appear as follows:
<google>ADSDAQBOX_FLOW</google>
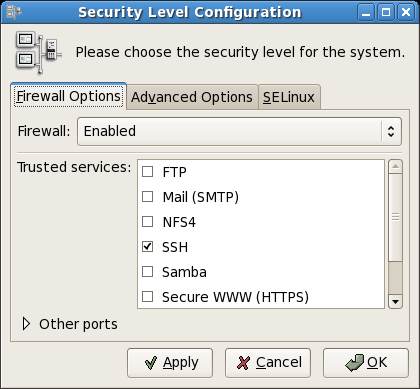
Notice that Fedora Linux enables the firewall by default, and allows only SSH access. This follows the general rule of security that a system should start with as much locked down as possible, and then lifted gradually to provide only the functionality needed, and nothing more.
Understanding the Firewall Settings
The first setting in the Firewall Options screen specifies whether the firewall is enabled or disabled. Unless the machine is not connected to network, or is behind a sophisticated firewall, this setting should always be set to Enabled.
The second section of the screen controls access to a number of different services which may or may not be running on your Fedora Linux system. Descriptions of these are as follows:
SSH - The secure shell provides an encrypted mechanism for allowing password protected remote access to your system. With SSH you can remotely log into to your system, copy files to and from your system and another systems and perform remote execution of programs. If you need remote access to your system you will need to activate this. If you do not need remote access leave this disabled. Note that the ssh server is not installed by default on Fedora Linux.
Telnet - Telnet provides remote terminal access to your system. It does not use encryption and use is strongly discouraged. Leave this disabled and use SSH instead for remote access.
WWW (HTTP) - If you are hosting a web server on your Fedora Linux System you will need to enable HTTP traffic through the firewall to enable web page requests to reach the http server. If you do not plan to host a web server, leave this disabled. Note that the Apache web server is not installed by default on Fedora Linux unless you specifically requested during the installation process.
Mail (SMTP) - Specifies whether the firewall blocks Simple Mail Transfer Protocol traffic. This is only necessary if you are hosting a mail server on your Fedora Linux system. If you only use a mail client to download email from a POP3 or IMAP server you can safely leave this disabled. Note that the SMTP server is not installed by default on Fedora Linux.
FTP - Controls whether File Transfer Protocol traffic is permitted through the firewall. Unless you plan to set up an ftp server (unlikely for typical users) leave this option disabled. Note that the FTP server is not installed by default on Fedora Linux.
Samba - The Samba service is allows files and printers to be shared between Linux and Windows systems. If this traffic is blocked in the firewall, it will not be possible to use Samba on this system.
To activate or deactivate a option use the simply click on the check box next the to service.
To configure the firewall for other services, click on the down arrow next to the Other ports label and click on the "Add" button. In the resulting dialog enter the port number to open. For example, to allow DNS traffic you would specify port 53.
Summary
This chapter has covered the basics of Fedora Linux firewall configuration.



