Configuring Windows Server 2008 DHCP Servers
Installing the DHCP Server Role
The first step in setting up a DHCP server on a Windows Server 2008 system is to install the DHCP Server feature on any servers with are required to provide the service. Before performing even this initial task, it is highly recommended that any systems designated to act as DHCP servers be assigned a static IP address. If the server is currently obtaining a dynamic IP address from another DHCP server, begin the installation process by assigning the system a static IP address. This can be achieved by launching the Server Manager and clicking View Network Connections. Right click on the network adapter on which the DHCP service is to be run and select Properties where either, or both the IPv4 or IPv6 address may be changed from automatically obtaining an IP address to specifying a static address. Once configured, exit from the properties dialog and network connections window leaving the Server Manager running.
Installation of the DHCP Server Role is performed by selecting Roles from the tree in the left hand pane of the Server Manager tool. On the Roles page, click on the Add Role link to launch the Add Roles Wizard. Dismiss the welcome screen if it is displayed, and in the Select Server Roles screen select the check box next to DHCP Server before clicking the Next button, read the information provided and click Next again to proceed to the Network Connection Binding screen. It is wihitn this screen that the DHCP server is associated with specific network adapters installed in the system. Select the network adapters for which the DHCP service will be provided and click Next.
DHCP can be used not just to provide clients with an IP address, but also additional information such as the name of the parent domain (for example techotopia.com) and the IP addresses of both preferred and alternate DNS servers. If the DHCP is required to provide these details for IPv4 clients, enter them into the Specify IPv4 DNS Server Settings page and click Next.
On the IPv4 WIN Server Settings page, enter addresses of the Preferred and Alternate WINS servers if required. Otherwise, leave the WINS is not required for applications on this network option selected and proceed to the next configuration page.
The next page allows initial DHCP scopes to be configured. A DHCP scope defines one or more ranges of IP addresses from which an IP address may assigned to a client and the duration of of the IP address lease (6 days for wired clients and 8 hours for wireless clients). This may either be configured now, or at a later point in the configuration process. The topic of defining DHCP scopes is covered in the Defining DHCP Scopes section of this chapter.
With the initial DHCP IPv4 configuration steps completed, the wizard subsequently moves on the the IPv6 settings. This is where a little background information is useful. Windows Server 2008 supports two modes of IPv6 DHCP operation, known as stateless and stateful. In stateful mode, clients obtain both an IP address and other information (such as DNS addresses) though the DHCPv6 server. In stateless mode, the clients receive only the non-IP address information from the DHCPv6 server. In this case, the IP address must be provided using some other mechanism, either by configuring of static IP addresses or through the implementation of IPv6 auto-configuration.
On the Configure DHCPv6 Stateless Mode screen, select either stateful or stateless mode in accordance with your specific enterprise requirements. If stateless mode is selected the next screen will prompt for the IPv6 DNS information to be provided to clients. Enter the information and click on Next. If the DHCP is part of an Active Directory domain, the Authorize DHCP Server page will appear. Enter the credentials (either your own as shown, or alternate credentials via the Alternate Credentials button) necessary to authorize the new DHCP server. Alternatively, the authorization may be performed later by skipping this step by clicking on Next.
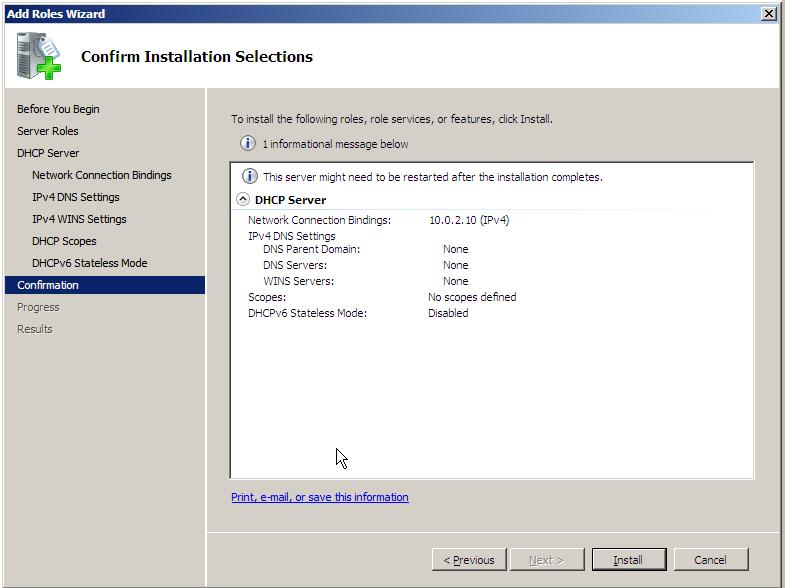
Upon completion of the DHCP server configuration the summary screen will displayed similar to the one illustrated below:
Assuming that the summarized configuration is correct, click on Install to complete the installation process. The wizard will display the progress of the DHCP Server Role installation before displaying a results screen confirming the successful installation. Once installation is complete, the DHCP Server may be managed locally or remotely using the DHCP console (Start -> All Programs -> Administrative Tools -> DHCP).
Authorizing DHCP Servers in Active Directory
If a DHCP server is to operate within an Active Directory domain (and is not running on a domain controller) it must first be authorized. This can be achieved either as part of the DHCP Server role installation, or subsequently using either DHCP console or at the command prompt using the netsh tool.
If the DHCP server was not authorized during installation, invoke the DHCP console (Start -> All Programs -> Administrative Tools -> DHCP), right click on the DHCP to be authorized and select Authorize. To achieve the same result from the command prompt, enter the following command:
netsh dhcp server serverID initiate auth
In the above command syntax, serverID is replaced by the IP address or full UNC name of system on which the DHCP server is installed.
Understanding DHCP Scope Types
DHCP scopes are used to define ranges of addresses from which a DHCP server can assign IP addresses to clients. Scopes fall into Normal, Multicast and Superscope categories as follows:
Normal Scope - Allows A, B and C Class IP address ranges to be specified including subnet masks, exclusions and reservations. Each normal scope defined must exist within its own subnet.
Multicast Scope - Used to assign IP address ranges for Class D networks.Multicast scopes do not have subnet masks, reservation or other TCP/IP options. Multicast scope address ranges require that a Time To Live (TTL) value be specified (essentially the number of routers a packet can pass through on the way to its destination).
Superscope - Essentially a collection of scopes grouped together such that they can be enabled and disabled as a single entity.
Configuring IPv4 Scopes Using the DHCP Console
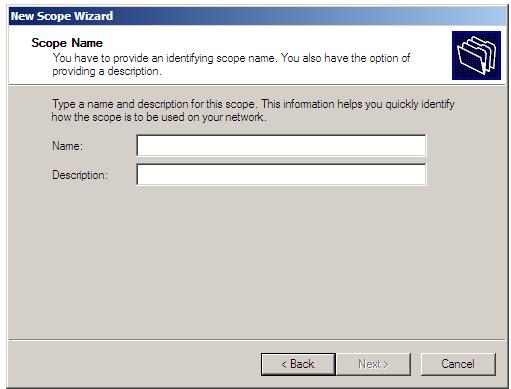
New scopes on Windows Server 2008 can either be configured from the graphical DHCP console, or from the command prompt using the netsh utility. To create a new scope in the DHCP console (launched from Start -> All Programs -> Administrative Tools -> DHCP) click on the server name in left hand panel so that IPv4 and IPv6 categories are listed in the main panel. Right click on the required IP version and select New scope from the menu top invoke the New Scope Wizard. Click on Next to skip the welcome screen so that the Scope Name dialog is displayed:
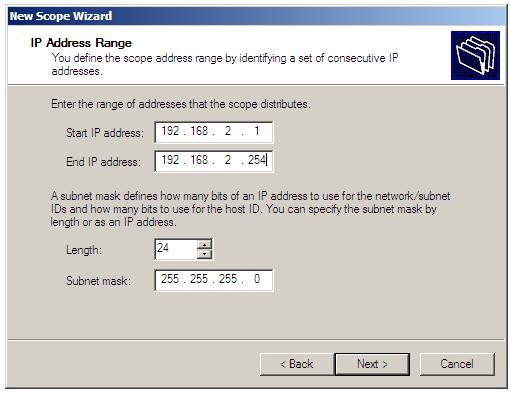
Enter a suitable name and description for the scope and press Next to proceed to the IP Address Range screen. In this screen, enter the start and end addresses of the IP address scope followed by the subnet mask, either in terms of bit length or in IP format (for example 255.255.255.0 or 24 bits). Note that when the start and end addresses are entered the subnet mask fields are filled in automatically, but may be changed manually if required:
If the address range specified encompasses multiple subnets (for example 192.168.2.1 through to 192.168.3.254) the wizard will warn that the designated range is too large for a single scope and provide the option to create a superscope made up of a number of different scopes depending on how many subnets are contained within the range.
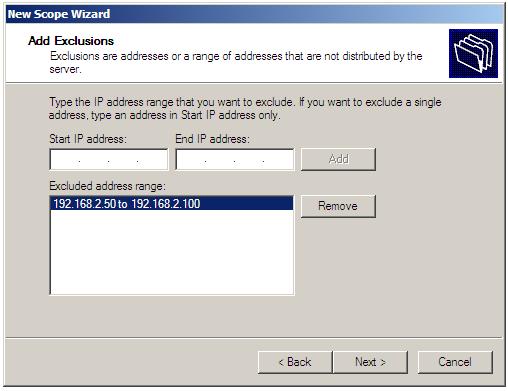
Assuming that all addresses in the scope range are on the same subnet, the wizard will provide the option to specify exclusions within the scope. Exclusions are essentially a ranges of one or more IP addresses within the defined scope which are not available for assignment to clients. Multiple exclusion ranges may be defined within a single scope by using the Add button to add new ranges:
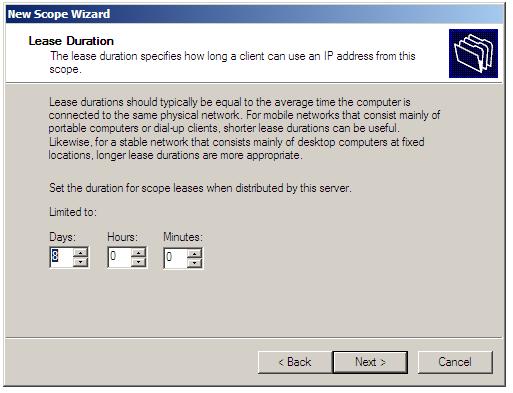
the next screen of the New DHCP Scope wizard relates to the topic of Lease Duration for the IP addresses in the current scope. Lease duration refers to the amount of time an IP address is assigned to a particular client computer or device. If the subnet on which the DHCP server operates has a high turnover of clients then a short lease is recommended (since the server will end up holding IP addresses for clients which are no longer connected, potentially exhausting the pool of IP addresses). For subnets where the connected clients are fairly stable, longer leases might be more appropriate. To define a lease duration use the spin boxes provided, specifying the duration in units of days, hours and even minutes (the default is 8 days):
The next screen provide the option to configure DHCP options (such as default gateway, DNS and WINS servers) which will be provided to clients along with the dynamic IP address. If the yes option is selected, the wizard will present a series of screens where these options may be specified if required. On each screen enter the appropriate information, or leave the page blank if the option is required (for example not all configurations require a WINS server). If "no" is selected the wizard will skip to the Activate Scope screen where, as the name suggests, the new scope may be activated. Once activated the wizard may be closed. The new scope is now defined and active.
Configuring Scopes at the Command Prompt
DHCP scopes may also be configured from the command prompt using the netsh tool. netsh may be run as a single command, or interactively. To run interactively. To run in interactive mode follow these steps:
1. At the command prompt enter netsh.
2. At the netsh> prompt enter dhcp.
2. At the netsh dhcp> prompt enter server \\servername where servername is the UNC name or IP address of the server to be managed. For example:
netsh dhcp>server \\windserver-1
3. At the netsh dhcp server prompt, enter the commands to be executed.
Alternatively, run each netsh command separately, using the following syntax:
netsh dhcp server \\servername commands
To create a new DHCP scope:
netsh dhcp server \\servername scope subnetID add iprange startIP endIP
For example, to create a scope on subnet 192.168.2.0 ranging from 192.168.2.1 through 192.168.2.100:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 add iprange 192.168.2.1 192.168.2.100 Changed the current scope context to 192.168.2.0 scope. Command completed successfully.
To list a scope IP address range:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 show excluderange Changed the current scope context to 192.168.2.0 scope. ========================================================= Start Address - End Address - Address type ========================================================= 192.168.2.1 - 192.168.2.100 - DHCP ONLY Number of IP Ranges : 1 in the Scope : 192.168.2.0. Command completed successfully.
To delete a scope using netsh:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 delete iprange 192.168.2.1 192.168.2.100 Changed the current scope context to 192.168.2.0 scope. Command completed successfully.
To display the current state of a scope:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 show state Changed the current scope context to 192.168.2.0 scope. Current State of the Scope 192.168.2.0 : Active Command completed successfully.
To add an exclude range to a scope:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 add excluderange 192.168.2.10 192.168.2.20 Changed the current scope context to 192.168.2.0 scope. Command completed successfully.
To display an exclude ranges:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 show excluderange Changed the current scope context to 192.168.2.0 scope. ===================================== Start Address - End Address ===================================== 192.168.2.10 - 192.168.2.20 Number of ExcludeRanges : 1 in the Scope : 192.168.2.0. Command completed successfully.
To list the clients using a DHCP scope:
netsh dhcp server \\winserver-1 scope 192.168.2.0 show clients