Sharing Ubuntu Linux Folders with Remote Windows Systems
| Previous | Table of Contents | |
| Sharing Ubuntu Linux Folders with Remote Linux and UNIX Systems |
Although Linux is increasingly making inroads into the desktop market, its origins are very much server based. It is not surprising therefore that Linux has the ability to act as a file server. It is also extremely common for Linux and Windows systems to be used side by side both in home and business environments. It is vital, therefore, that files on a Linux system be accessible to both Linux, UNIX and Windows based systems over network connections. Similarly, shared folders residing on Windows systems must also be accessible from Ubuntu systems.
Windows systems share resources such as file systems and printers using something called Server Message Block (SMB). In order for a Linux system to serve such resources over a network to a Windows system and vice versa it must, therefore, support SMB. This is achieved using Linux based technology called Samba. In addition to providing integration between Linux and Windows systems, Samba may also be used to provide folder sharing between Linux systems (as an alternative to NFS which was covered in Sharing Ubuntu Linux Folders with Remote Linux and UNIX Systems).
In this chapter we will look at the steps necessary to share file system resources and printers on an Ubuntu system with remote Windows and Linux systems.
Setting Up Ubuntu Linux/Windows File Sharing
The sharing of Linux folders with Windows based systems is not installed and configured by default on Ubuntu. Fortunately, attempting to share folders will automatically trigger the installation of the appropriate services.
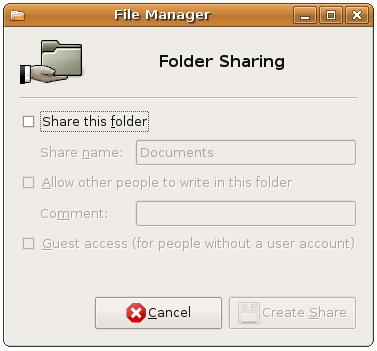
To begin the process of sharing, open a file browser window by selecting, for example, Places->Home Folder. Navigate using the file browser until the folder to be shared is visible. Right click on the icon for this folder and select Sharing Options' from the resulting menu to invoke the following dialog: <google>ADSDAQBOX_FLOW</google>
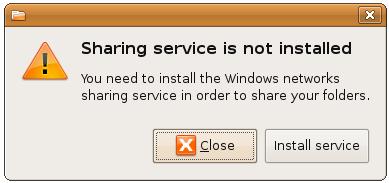
To enable folder sharing, set the Share this folder option. If the folder sharing service has not previously been installed, the following dialog will appear seeking permission to install the service:
Click Install, enter your password and wait for the installation to complete. Once the installation is finished it will be necessary to log out of the current desktop session and log back in again before the changes take effect.
Sharing Ubuntu Linux Folders
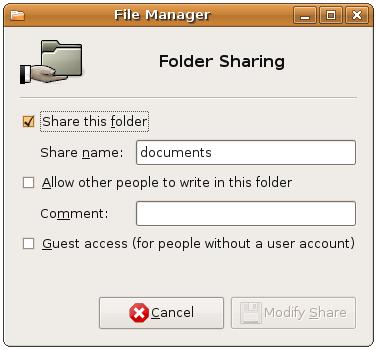
Once the folder sharing services are installed, the next step is to share a folder. Once again, open a file browser, locate a suitable folder, right click on it and select Sharing Options. This time the Sharing Options dialog will appear with a number of configuration options available for editing:
The configuration options provided in this dialog are as follows:
- Share this folder - When selected, this option makes the folder available to other Windows and Linux systems on the network.
- Share name - The share name by which the folder will be referenced by Windows systems.
- Allow other people to write to this folder - Controls whether users accessing the folder remotely have read-only or read/write access to the folder.
- Guest access - Allows remote users who do not have an account on the local system to access the shared folder.
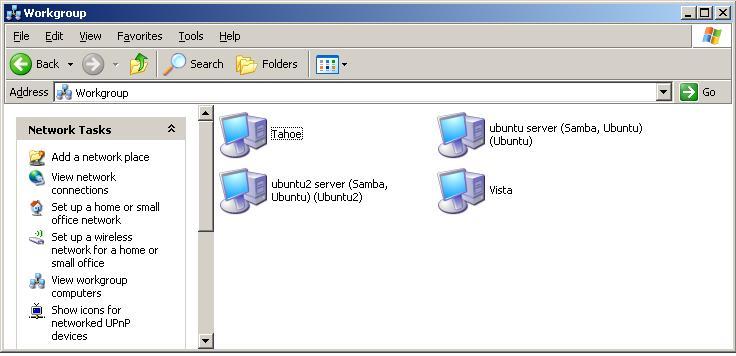
Once completed, the folder you specified will be visible from any Windows systems on the same network as your Ubuntu system. You should now have remote access to your Linux folder from the Windows system. To access the folder, open the Windows Network browser and navigate to Workgroup where any Ubuntu systems with shared folders should be listed as illustrated in the following figure:
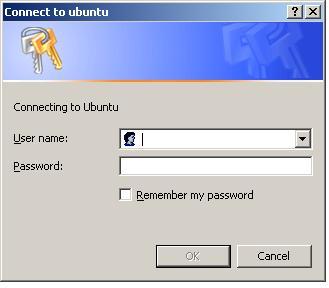
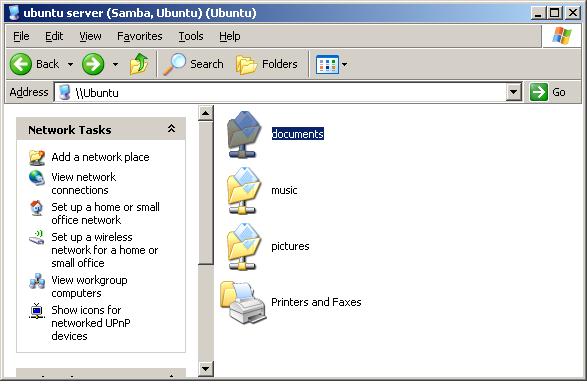
Double click on an Ubuntu system to access the shared folders, entering a suitable username and password if prompted to do so:
Once a valid username and password have been entered, any shared folders configured on the Ubuntu system will be listed in the Windows Explorer dialog ready for access:
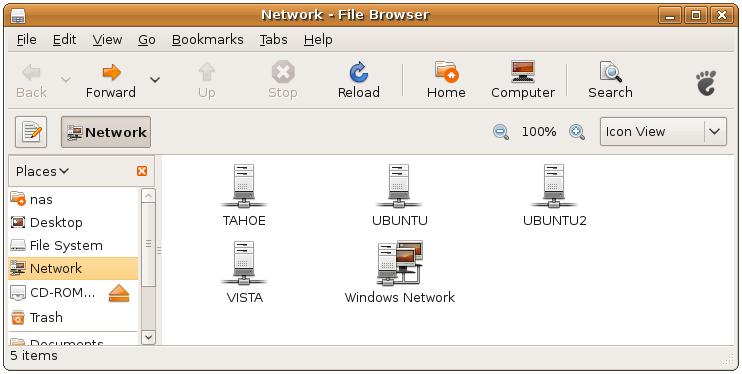
To access a shared folder from an Ubuntu system, select the Places->Network menu option. Once loaded, the browser will list all systems on the network as illustrated in the following figure:
To access a shared folder and its contents, simply double click on the corresponding host to view a list of available shared folders.
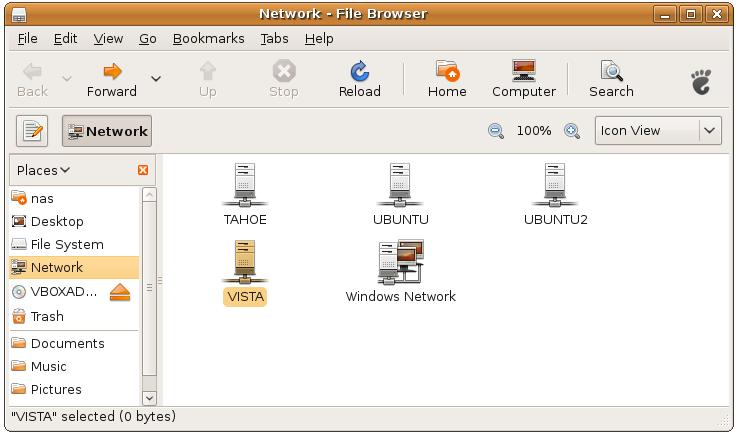
As previously discussed, Samba not only makes it possible for Windows clients to access shared folders hosted on an Ubuntu system, it also allows the Ubuntu system to access shared folders and printers residing on a Windows system. To access Windows shared resources, open the Ubuntu Places->Network browser to review the list of available systems. The example in the following figure shows a number of systems available on the network, one of which has clearly been named to indicate it is running Windows Vista:
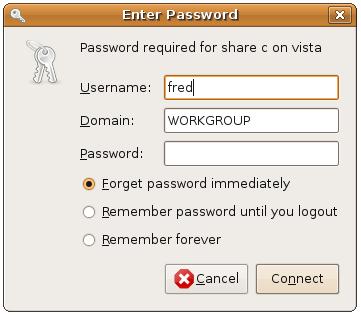
Double clicking on a Windows system in the browser (in this case the system named Vista) will display a list of printers, folders and disk drives on the Windows system that are available to the Ubuntu system. Double on a folder will either display the contents of the folder, or prompt for a valid user name and password on the Windows system:
Once the credentials have been entered into the text fields in the above dialog, options are available to store the credentials so that they need to be re-entered each time the resource is accessed, do not need to entered again during the current session or are not required ever again.