Auditing Windows Server 2008 File and Folder Access
In order to track file and folder access on Windows Server 2008 it is necessary to enable file and folder auditing and then identify the files and folders that are to be audited. Once correctly configured, the server security logs will then contain information about attempts to access or otherwise manipulate the designated files and folders. It is important to note that file and folder auditing is only available for NTFS volumes.
Enabling File and Folder Auditing
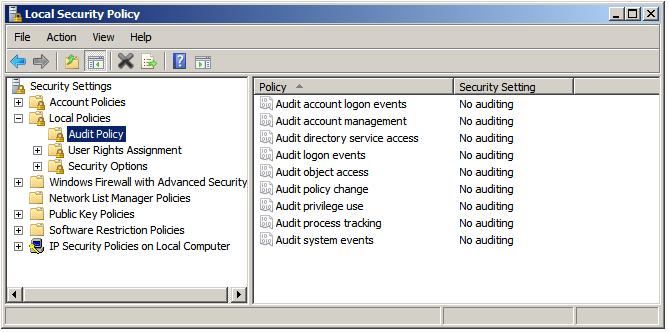
File and folder auditing is enabled and disabled using either Group Policy (for auditing domains, sites and organizational units) or local security policy (for single servers). To enable file and folder auditing for a singe server, select Start -> All Programs -> Administrative Tools -> Local Security Policy. In the Local Security Policy tool, expand the Local Policies branch of the tree and select Audit Policy.
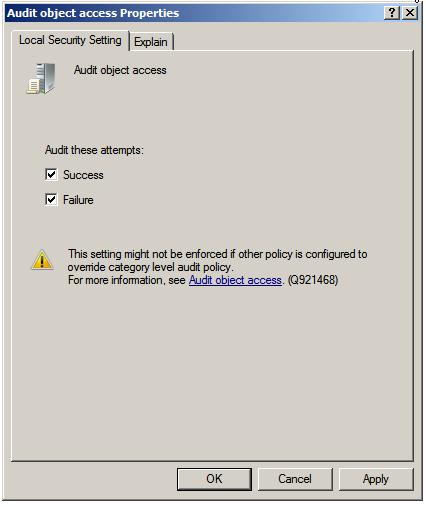
Double click on the Audit Object Access item in the list to display the corresponding properties page and choose whether success, failed, or both types of access to files or folder is to be audited:
Once the settings are configured click on Apply to commit the changes and then OK to close the properties dialog. With file and folder auditing enabled the next task is to select which files and folders are to be audited.